|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Abstract
Mohammad Mehdi Ardabili’s Principles of Struggle1 in the Age of Nihilism offers a bold and multifaceted critique of modernity’s epistemological and ontological frameworks. By addressing the pervasive impact of nihilism, Ardabili constructs a dual-phased project: deconstructing traditional assumptions about reality and knowledge while providing practical exercises to rebuild meaning and action in a post-nihilistic world. This article explores Ardabili’s philosophical contributions, critiques of realism, and the innovative solutions he proposes to navigate the challenges of nihilism in contemporary thought.
Introduction
Nihilism, as both a philosophical condition and a cultural phenomenon, has shaped the trajectory of modern thought. Mohammad Mehdi Ardabili confronts this challenge in Principles of Struggle in the Age of Nihilism, offering a framework that moves beyond despair. He situates his project within the intellectual lineage of Kant, Nietzsche, and postmodern thinkers, critiquing the foundations of realism and scientific certainty. Ardabili not only challenges the dominant paradigms but also outlines a positive path forward through allegorical systems and mental exercises aimed at empowering individuals in the face of existential crises.
The Dual Framework: Deconstruction and Reconstruction
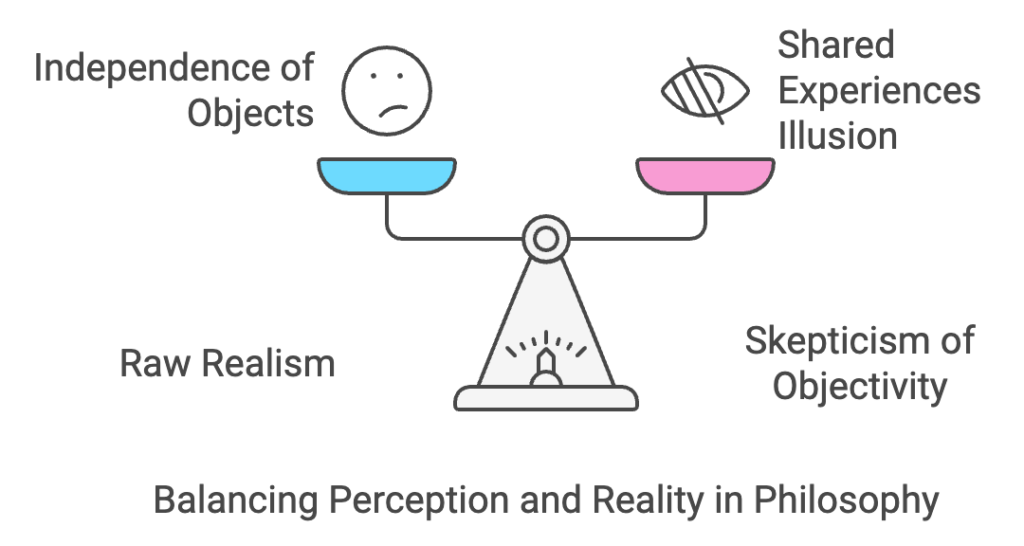
1. The Negative Aspect: Critique of Realism Ardabili’s work begins with a systematic critique of realism, the dominant assumption that objects and their properties exist independently of the observer. Drawing on Kantian epistemology, he dismantles the notion of an unmediated relationship between the subject and the object. He emphasizes that perception is inherently shaped by cognitive systems, making the so-called “reality” an illusion shaped by our mental and sensory mechanisms.
Key critiques include:
- Raw Realism: Ardabili argues that most humans, including scientists and philosophers, operate under a naïve belief in the independence of objects from subjective perception.
- Skepticism of Objectivity: He critiques the tendency to equate shared human experiences (e.g., color perception) with objective reality, highlighting the role of shared cognitive structures in perpetuating illusions.
2. The Positive Aspect: Reconstructing Meaning While Ardabili’s critique is radical, his project does not end with deconstruction. He proposes practical and theoretical solutions to navigate a post-nihilistic world:
- Allegorical Systems: Ardabili views myths, stories, and allegories as central to human cognition. He repositions these systems as tools for meaning-making rather than mere remnants of premodern thought.
- Exercises in Consciousness: To counter the automatic storytelling of the mind, he advocates for practices that disrupt habitual narratives, allowing individuals to confront the raw experience of existence without preconceptions.
Philosophical Innovations
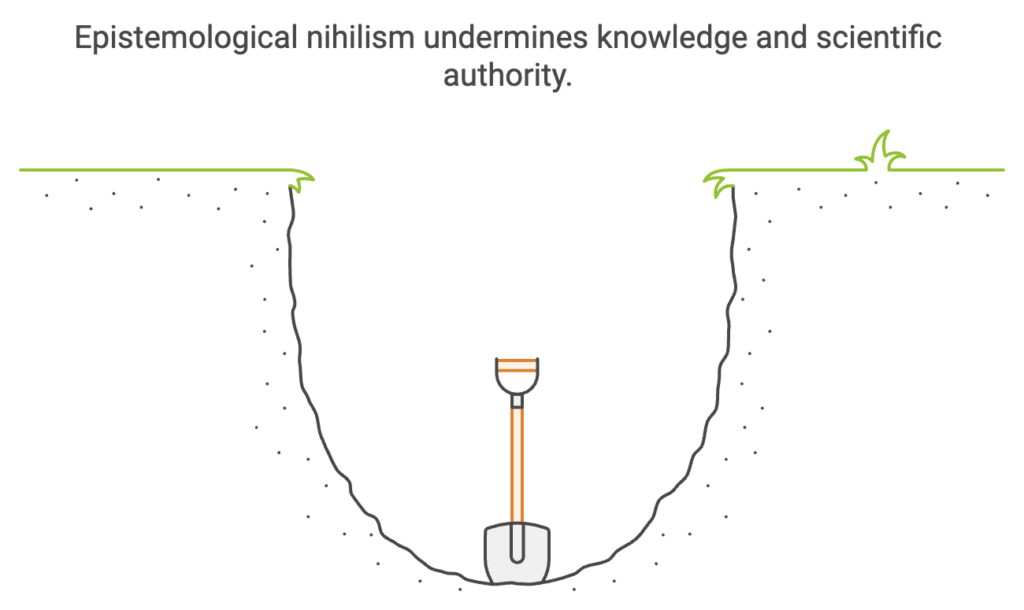
1. Epistemological Nihilism Ardabili identifies epistemological nihilism as a critical challenge of our era. This condition, characterized by a radical skepticism of all knowledge systems, is not merely a critique but an opportunity for transformation. Ardabili’s framework acknowledges the impossibility of accessing absolute truth while proposing coherence, pragmatism, and humility as alternative evaluative criteria.
2. Critique of Scientism In one of his most provocative sections, Ardabili critiques the overreach of science, which he labels “scientism.” He highlights:
- The focus on efficiency over truth-seeking.
- The role of power dynamics, including corporate and military interests, in shaping scientific agendas.
- The dangers of reducing human experience to quantifiable metrics.
3. Allegorical Storytelling as a Cognitive Tool Ardabili’s concept of allegorical systems redefines the role of myths and stories in human cognition. By framing these narratives as tools for navigating existential wonder, he elevates their status from primitive beliefs to sophisticated cognitive frameworks that can guide action and thought in a post-nihilistic age.
Practical Applications
1. Mental Exercises Ardabili proposes exercises aimed at disrupting automatic mental processes. These practices help individuals step outside the bounds of conventional narratives, fostering creativity and resilience in the face of nihilism.
2. Frameworks for Action His principles are not confined to abstract philosophy but are designed to guide individuals and societies in constructing systems of meaning that are coherent, pragmatic, and adaptable.
3. Humility and Critique Ardabili’s emphasis on humility is a central ethical component of his work. By acknowledging the limits of human knowledge, he advocates for a more inclusive and open-ended approach to philosophical and scientific inquiry.
Implications for Contemporary Thought
Ardabili’s work resonates with pressing questions in philosophy, science, and culture:
- For Philosophy: His radical skepticism challenges foundationalist approaches while offering a practical methodology for navigating uncertainty.
- For Science: Ardabili’s critique of scientism highlights the need for science to reclaim its ethical and exploratory dimensions beyond technological domination.
- For Culture: His emphasis on storytelling and allegories as cognitive tools has implications for education, media, and the arts, suggesting new ways to engage with meaning-making in an increasingly fragmented world.
Summary of the Book
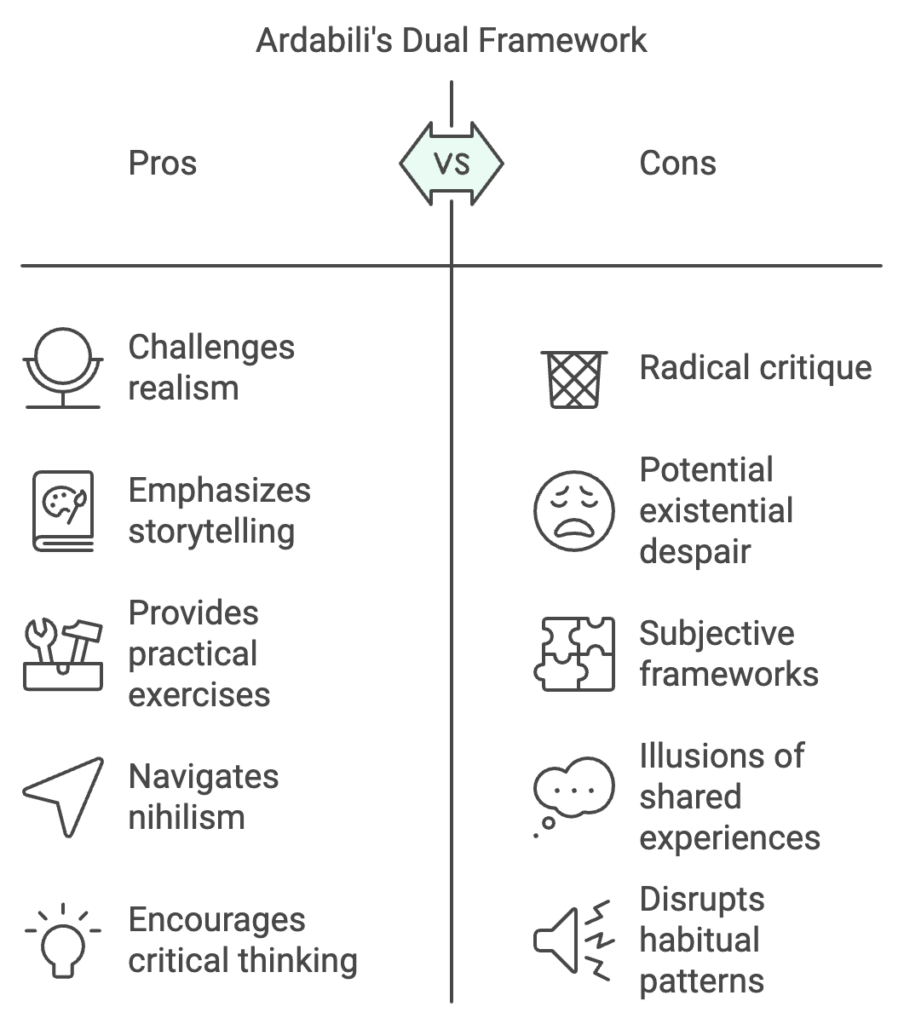
The book is structured around a dual framework: a rigorous deconstruction of traditional systems of thought and a constructive methodology for rebuilding meaning. Ardabili’s approach moves beyond despair, offering tools to confront nihilism directly and creatively.
- Deconstruction: The Negative Aspect
- Ardabili critiques the dominant epistemological and ontological assumptions of modernity, particularly realism, which posits the independence of objects from the observer.
- He argues that perception and knowledge are inherently shaped by subjective frameworks, challenging the notion of objective reality.
- Drawing on Kant, he explores the role of the cognitive apparatus in constructing what we perceive as reality, asserting that shared experiences are often illusions reinforced by collective conditioning.
- Reconstruction: The Positive Aspect
- While his critique is radical, Ardabili does not leave the reader in existential despair. He proposes “allegorical systems” as a means of navigating a world without absolute truths.
- These systems emphasize the importance of storytelling and myth as tools for meaning-making, advocating for their creative and critical use.
- Practical exercises are provided to disrupt habitual mental patterns, empowering individuals to think and act beyond established narratives.
Key Themes
- The Critique of Realism Ardabili takes aim at the belief that reality exists independently of human perception. He deconstructs this assumption through historical and philosophical analysis, showing how realism has dominated both scientific and cultural thought. His critique is not merely academic but deeply personal, challenging readers to question their own perceptions of the world.
- Epistemological Nihilism The book delves into the crisis of knowledge in the modern era, addressing the limitations of human understanding. Ardabili reframes nihilism as an opportunity for transformation rather than a cause for despair, urging readers to embrace uncertainty as a foundation for creativity.
- The Role of Science and Scientism Ardabili’s critique of scientism is one of the book’s boldest features. He highlights the limitations of science when it becomes overly focused on efficiency and power rather than truth-seeking. This critique challenges readers to reconsider the ethical and philosophical foundations of modern scientific practice.
- Storytelling as a Cognitive Tool By positioning storytelling and allegory as central to human cognition, Ardabili offers a framework for meaning-making that transcends traditional metaphysics. He views myths, narratives, and allegories as essential tools for navigating the complexities of existence in a post-nihilistic age.
Strengths of the Book
- Intellectual Depth Ardabili’s work is steeped in philosophical rigor, engaging with complex ideas from thinkers like Kant, Nietzsche, and Adorno. His analysis of realism and nihilism is both comprehensive and original, offering fresh perspectives on age-old debates.
- Practical Relevance Unlike many philosophical works, Principles of Struggle in the Age of Nihilism is not confined to abstract theorizing. The inclusion of practical exercises and methodologies makes the book accessible to a wider audience, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
- Challenging and Provocative Ardabili’s critique of scientism and his call for humility in the face of existential wonder are both timely and provocative. His willingness to question foundational assumptions in philosophy, science, and religion invites readers to think deeply and critically about their own beliefs.
Critique of the Book
- Dense and Complex The book’s philosophical depth may prove challenging for readers without a background in philosophy. Some sections, particularly those critiquing realism and epistemology, require careful and repeated reading to fully grasp.
- Lack of Specific Case Studies While the book offers practical exercises, it occasionally lacks concrete examples or case studies that could illustrate its principles in action. More real-world applications would enhance its accessibility.
Conclusion
Mohammad Mehdi Ardabili’s Principles of Struggle in the Age of Nihilism is both a critique and a call to action. By dismantling the illusions of realism and scientism, he lays the groundwork for a new philosophical approach that embraces the challenges of nihilism. His dual framework of deconstruction and reconstruction offers individuals and societies tools to navigate existential crises and build coherent systems of meaning. As nihilism continues to shape the intellectual and cultural landscape, Ardabili’s work provides a vital roadmap for the future.
References
- Ardabili, Mohammad Mehdi. Principles of Struggle in the Age of Nihilism.
- Kant, Immanuel. Critique of Pure Reason.
- Nietzsche, Friedrich. The Will to Power.
- Adorno, Theodor. Negative Dialectics.
Footnotes:
- The term “struggle” has been used as a translation for the original term “fighting” to better capture the philosophical depth and nuance of Ardabili’s framework in the context of confronting nihilism.
- At the time of writing, the English version of Principles of Struggle in the Age of Nihilism is not yet available in its entirety; only the prologue has been translated and published.
- If you read to here, check out How to navigate uncertainty, my personal opinion about the concept
